The Registry Infrastructure
Topic Summary (TL;DR)
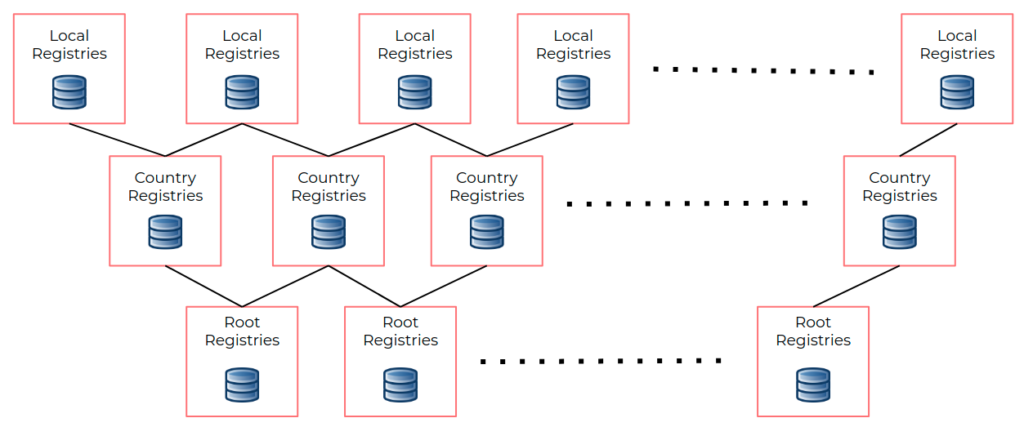
The Registry Infrastructure layer comprises a network of open registries that store detailed information about every network participant. The registries are maintained by entities called “Registration Platforms”.
The candidates for BAPs or BPPs submit the relevant credentials to the Registration Platform and, until approved, have the status of registrants. Approved registrants obtain INITIATED status and are called “subscribers”.
The Registry Infrastructure layer consists of a network of open registries that store detailed information about every network participant.
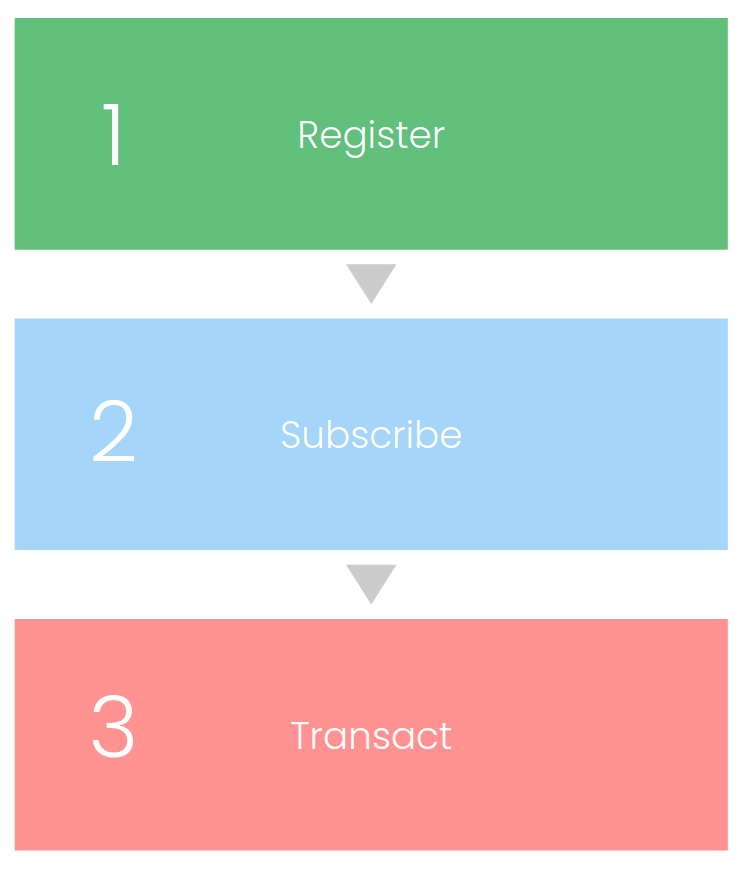
To get listed on a registry, there is a there is a procedure which is mandatory for every network participant. The registration (in terms of requirements) is specific to each beckn-enabled network. The actors in the Registry Infrastructure layer are the
- Registration Platform(s) — the Registration Platform is a trusted entity that maintains the registry of the participants on the network. Registration Platforms can be formed by the participants of the network or by a public authority; this depends on nature of the network. A network can have more than one such registration platform, all operating by the same rules.
- Registrant — any business or non-profit entity that wants its platform to be listed on the Registry. To be listed, the registrant must submit relevant credentials to the Registration Platform. A registrant can apply to be a Beckn Application Platform (BAP), Beckn Provider Platform (BPP), or Beckn Gateway (BG) or any other role allowed in the network.
- Subscriber — after the registrant is approved by the Registration Platform, it is listed on the registry with INITIATED status. From this moment on, the entity being registered in no longer a registrant and becomes a subscriber. The subscriber status gives the entity the right to perform transactions on the network.
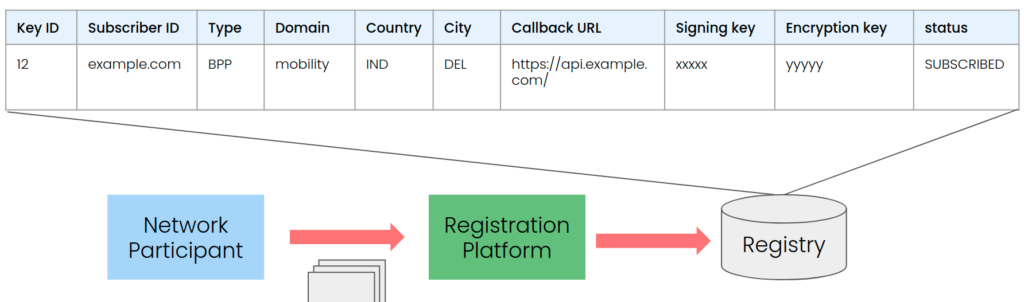
This a sample subscriber record in a registry database:
Any receiver of an API request must authenticate the sender by looking up the network registry and verify the signature of the sender through the sender’s public key.









